PSAT/NMSQT
How to Access your PSAT/NMSQT Scores
If you provided your email address on your answer sheet on test day, you’ll receive an email notifying you of when your scores are available. The email will have a unique access code that will connect you to your scores online. If you didn’t provide an email address on your answer sheet on test day, you can still access your scores online. Note: In either instance, if you haven’t already done so, you’ll be asked to set up a free College Board account before you can view your scores.
Don’t have a College Board account? Save time and set one up now. DO NOT create a second account if you cannot get logged in to your original account. Call College Board and trouble shoot your username and password. You must check for verification emails using your GMail account, not Outlook.
Once you’ve received your scores, you can use them for practice, scholarship opportunities, and more. Need additional help? https://satsuite.collegeboard.org/psat-nmsqt/scores/getting-scores
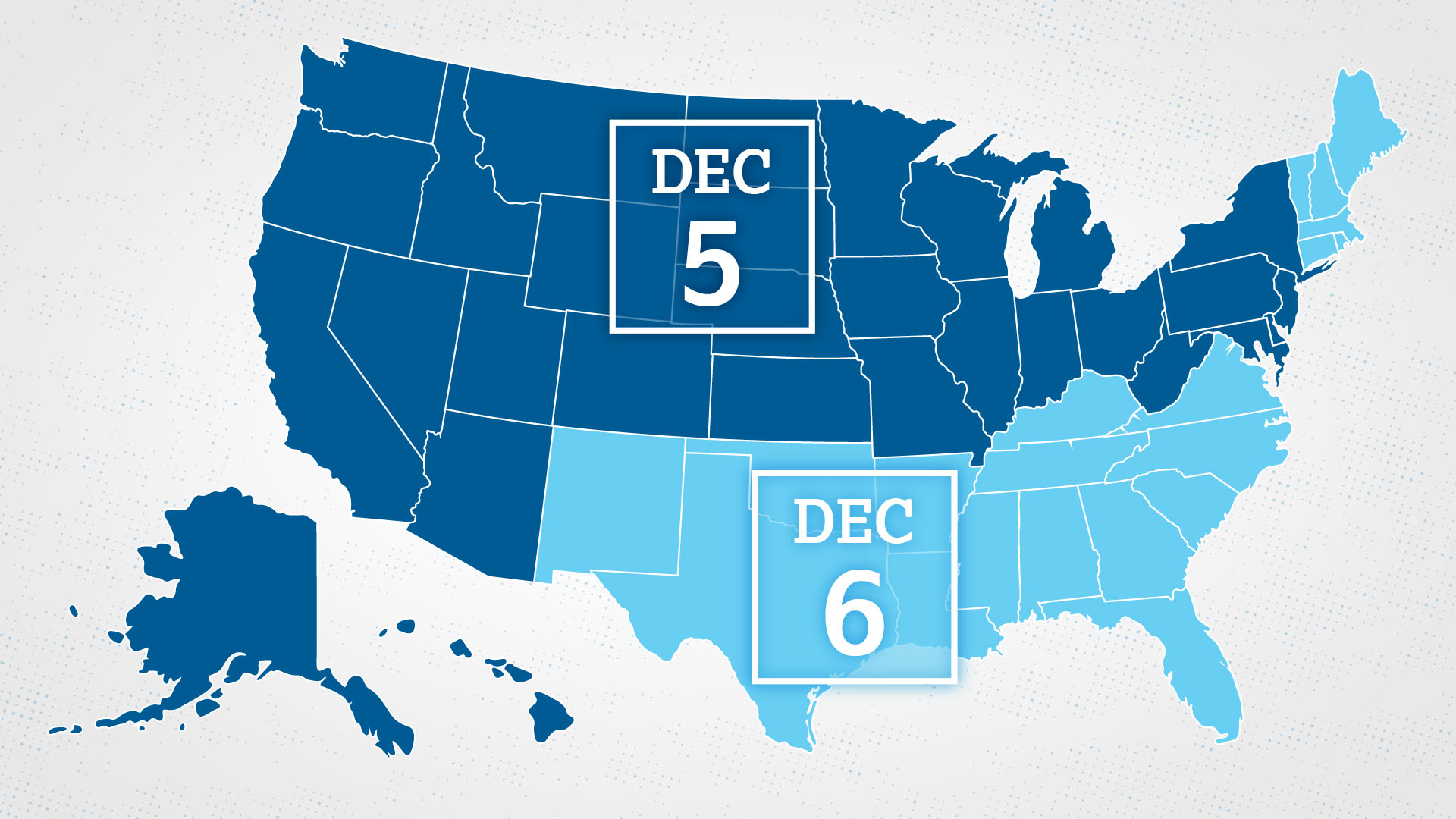
When to Expect Scores
Students get 2022 PSAT/NMSQT October test scores on December 5-6, 2022
How the PSAT/NMSQT Is Structured
The PSAT/NMSQT takes 2 hours and 45 minutes and consists of 3 tests: (1) the Reading Test, (2) the Writing and Language Test, and (3) the Math Test. Most of the questions are multiple choice, though some math questions ask you to write in the answer rather than select it.
The following table shows how much time you get for each test and the number of questions for each test:
|
Section |
Length (minutes) |
Number of Questions/Tasks |
|
Reading |
60 |
47 |
|
Writing and Language |
35 |
44 |
|
Math |
70 |
48 |
|
Total |
165 |
139 |
The Reading Test Overview
The Reading Test presents five reading passages followed by multiple-choice questions about each passage. You have 60 minutes to complete this test, which includes 47 questions total. 
What the Reading Test Passages are Like
The five passages on the Reading Test include four standalone passages and one pair of passages that you read together. The standalone passages and the paired set are each 500–750 words. The passages are drawn from the following types of documents:
- 1 literary passage from a work of fiction.
- 1 or 2 passages from a U.S. founding document or a text in the Great Global Conversation they inspired. An example of a founding document would be the U.S. Constitution. The Great Global Conversation refers to works from around the world that focus on topics such as freedom, justice, or human dignity. A speech by Nelson Mandela would be an example.
- 1 passage from a work of economics, psychology, sociology, or some other social science.
- 2 passages from scientific works that examine foundational concepts and developments in Earth science, biology, chemistry, or physics.
What the Reading Test Questions are Like
The questions on the reading test fall into three broad categories:
1. How The Author Uses Evidence
Some questions ask you to show that you understand how an author is using evidence to support a claim. Questions like this might ask you to:
- Identify the part of a passage that supports a point the author is making.
- Find evidence in a passage that best supports the answer to a previous question.
- Find a relationship between an informational graphic and the passage it’s paired with.
2. Understanding Words in Context
Many of the questions on the Reading Test ask you to identify the meaning of a word in context. The “in context” part is important: the questions ask you to use context clues in a passage to figure out which meaning of a word or phrase is being used. Other questions will ask you to decide how an author’s choice of words shapes meaning, style, and tone.
3. Analysis in History/Social Studies and in Science
The Reading Test includes passages in the fields of history, social studies, and science. You’ll be asked questions that require you to draw on the reading skills needed most to succeed in those subjects. For instance, you might read about an experiment and then see questions that ask you to:
- Examine hypotheses.
- Interpret data.
- Consider implications.
The answers are based only on the content stated in or implied by the passage, not your prior knowledge of the subject.
PSAT/NMSQT Vocabulary
The PSAT/NMSQT doesn’t require you to learn unusual or difficult vocabulary words. The words you’ll be asked about come up often in college-level reading and in professional life.
In addition, the PSAT/NMSQT also doesn’t ask you to define a word without any context to guide you. All of the words you’ll be asked about appear in the context of reading passages, so you can use context clues to guide you to the best answer.
If you build your vocabulary by learning the meaning and usage of words that appear most often in college-level assignments, you’ll have a much easier time with the test. In particular, you won’t have to spend time guessing from context what a word might mean. If you recognize vocabulary words on sight, you’ll read passages faster and with greater confidence.
Practice identifying the meaning of words in context on Official SAT Practice at satpractice.org.
PSAT/NMSQT Writing and Language Test
The Writing and Language test is a multiple-choice test where you read passages, find mistakes and weaknesses, and fix them.
This part of the PSAT/NMSQT is 35 minutes long, includes 4 passages, and contains 44 multiple-choice questions. ![]()
What the Writing and Language Test Passages Are Like
The 4 passages on the test are each 400–450 words. The complexity of the passages varies: some are more challenging and others more straightforward.
The passages are about a variety of topics, including careers, science, the humanities, and history and social studies.
The purpose and format of each passage varies:
- At least 1 is a narrative, meaning it describes events in a storylike way. This passage is not a work of fiction, but it could be a nonfiction account of an historical event, or it might describe the sequence of events in a scientific experiment.
- The other passages are either argumentative, meaning they try to convince or persuade the reader of something, or else informative and explanatory.
Some of the passages contain charts, graphs, or infographics that you interpret together with the written part of the passage.
What the Writing and Language Test Questions are Like
Each passage has 11 multiple-choice questions.
The questions fall into two main types: those where you improve the expression of ideas, and those where you have to recognize and correct errors in sentence structure, grammar, usage, and punctuation.
Expression of Ideas
These questions ask you to improve the substance and quality of the writer’s message. They can be divided into three kinds:
- Development questions are about main ideas (topic sentences and thesis statements), supporting details, focus, and quantitative information in tables, graphs, and charts.
- Organization questions focus on logical sequence and placement of information and ideas as well as effective introductions, conclusions, and transitions.
- Effective Language Use questions ask you to improve precision and eliminate wordiness, consider style and tone, and combine sentences to improve flow and to achieve particular rhetorical effects (such as emphasizing one point over another).
Standard English Conventions
These questions focus on recognizing and correcting grammar, usage, and mechanics problems in passages. These questions ask you to recognize and correct errors in sentence structure (like run-on or incomplete sentences), usage (like lack of subject-verb or pronoun-antecedent agreement), and punctuation (like missing or unnecessary commas).
The Math Test Overview
The Math Test focuses on the areas of math that play the biggest role in a wide range of college majors and careers:
- Heart of Algebra, which focuses on the mastery of linear equations and systems.

- Problem Solving and Data Analysis, which is about analyzing problems and drawing information from data.
- Passport to Advanced Math, which features questions that ask you to manipulate complex equations.
- The Math Test also includes 2 questions from Additional Topics in Math, including the geometry and trigonometry most relevant to college and career readiness.
The Math Test is divided into two parts: a no-calculator portion and a calculator portion. In both portions, most of the test is multiple choice, but some of the questions at the end ask you to write the answer (these are called “grid-ins”).
Breakdown of the Math Test
|
No-Calculator Portion |
Calculator Portion |
|
|
Time allotted |
25 minutes |
45 minutes |
|
Total questions |
17 |
31 |
|
Multiple-choice questions |
13 |
27 |
|
Grid-in questions |
4 |
4 |
Types of Math Tested
|
Type of Math |
Number of Questions |
|
Heart of Algebra |
16 |
|
Problem Solving and Data Analysis |
16 |
|
Passport to Advanced Math |
14 |
|
Additional Topics in Math |
2 |
Heart of Algebra
Heart of Algebra focuses on linear equations, systems of linear equations, and functions. These questions ask you to create equations that represent a situation, solve equations and systems of equations, and make connections between different representations of linear relationships.
Heart of Algebra includes the following types of questions:
- Create, solve, or interpret a linear expression or equation in 1 variable.
- Create, solve, or interpret linear inequalities in 1 variable.
- Build a linear function that models a linear relationship between 2 quantities.
- Create, solve, and interpret systems of linear inequalities in 2 variables.
- Create, solve, and interpret systems of 2 linear equations in 2 variables.
- Algebraically solve linear equations (or inequalities) in 1 variable.
- Algebraically solve systems of 2 linear equations in 2 variables.
- Interpret the variables and constants in expressions for linear functions.
- Understand connections between algebraic and graphical representations.
Problem Solving and Data Analysis
Problem Solving and Data Analysis includes using ratios, percentages, and proportional reasoning to solve problems in real-world situations, including science, social science, and other contexts. It also includes describing relationships shown graphically and analyzing statistical data.
This group of skills is really about being quantitatively literate and demonstrating a command of the math that resonates throughout college courses, career training programs, and everyday life.
Problem Solving and Data Analysis includes the following types of questions:
- Use ratios, rates, proportional relationships, and scale drawings to solve single- and multistep problems.
- Solve single- and multistep problems involving percentages.
- Solve single- and multistep problems involving measurement quantities, units, and unit conversion.
- Use scatterplot, linear, quadratic, or exponential models to describe how the variables are related.
- Use the relationship between 2 variables to investigate key features of the graph.
- Compare linear growth with exponential growth.
- Use 2-way tables to summarize categorical data and relative frequencies and calculate conditional probability.
- Make inferences about population parameters based on sample data.
- Use statistics to investigate measures of center of data. Analyze shape, center, and spread.
- Evaluate reports to make inferences, justify conclusions, and determine appropriateness of data collection methods. The reports may consist of tables, graphs, or text summaries.
Passport to Advanced Math
Passport to Advanced Math is the third area of focus in the PSAT/NMSQT Math Test. This area focuses on math you need to pursue further study in a discipline such as science or economics and for career opportunities in the STEM fields of science, technology, engineering, and math.
The Passport to Advanced Math area requires familiarity with more complex equations or functions, which will prepare you for calculus and advanced courses in statistics.
Passport to Advanced Math includes the following types of questions:
- Create a quadratic or exponential function or equation that models a context.
- Determine the most suitable form of an expression or equation to reveal a particular trait, given a context.
- Create equivalent expressions involving rational exponents and radicals, which includes simplifying or rewriting in other forms.
- Create an equivalent form of an algebraic expression by using structure and fluency with operations.
- Solve a quadratic equation having rational coefficients. The equation can be presented in a wide range of forms to reward attending to algebraic structure and can require manipulation to solve.
- Add, subtract, and multiply polynomial expressions. Simplify the result. The expressions will have rational coefficients.
- Solve an equation in 1 variable that contains radicals or contains the variable in the denominator of a fraction.
- Solve a system of 1 linear equation and 1 quadratic equation.
- Rewrite simple rational expressions.
- Interpret parts of nonlinear expressions in terms of their context.
- Understand the relationship between zeros and factors of polynomials. Use that knowledge to sketch graphs.
- Understand a nonlinear relationship between 2 variables by making connections between their algebraic and graphical representations.
- Use function notation, and interpret statements using function notation.
- Use structure to isolate or identify a quantity of interest in an expression or isolate a quantity of interest in an equation.
Questions of this type may include the following:
- Solve problems using volume formulas.
- Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean theorem to solve applied problems involving right triangles.
- Add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify complex numbers.
- Convert between degrees. Use radians to determine arc lengths. Use trigonometric functions of radian measure.
- Apply theorems about circles to find arc lengths, angle measures, chord lengths, and areas of sectors.
- Use concepts and theorems about congruence and similarity to solve problems about lines, angles, and triangles.
- Use the relationship between similarity, right triangles, and trigonometric ratios. Use the relationship between sine and cosine of complementary angles.
- Create or use an equation in 2 variables to solve a problem about a circle in the coordinate plane.
Additional Topics in Math
The PSAT/NMSQT Math Test also contains two questions in Additional Topics in Math (one in the no-calculator portion and one in the calculator portion). The questions might include topics like geometry, trigonometry, radian measure, and complex numbers.
Questions of this type may include the following:
- Solve problems using volume formulas.
- Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean theorem to solve applied problems involving right triangles.
- Add, subtract, multiply, divide, and simplify complex numbers.
- Convert between degrees. Use radians to determine arc lengths. Use trigonometric functions of radian measure.
- Apply theorems about circles to find arc lengths, angle measures, chord lengths, and areas of sectors.
- Use concepts and theorems about congruence and similarity to solve problems about lines, angles, and triangles.
- Use the relationship between similarity, right triangles, and trigonometric ratios. Use the relationship between sine and cosine of complementary angles.
- Create or use an equation in 2 variables to solve a problem about a circle in the coordinate plane.
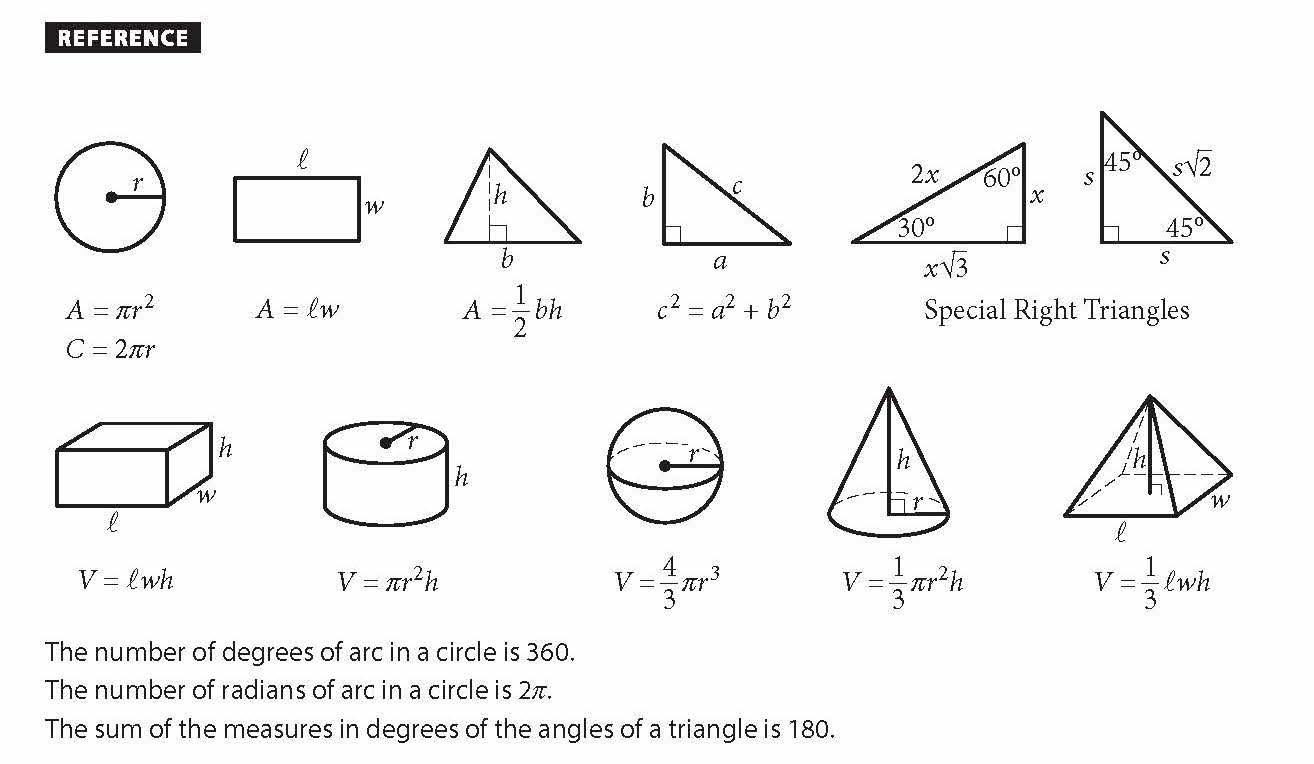
Reference Information
The following reference information is provided for you on the test. This information will be more helpful to you if you take time to be sure you understand all of it before the test. The tutorials at satpractice.org can help you brush up on any topics you feel unsure about.
PSAT/NMSQT Calculator Use
Calculators are important tools, and to succeed after high school, you’ll need to know how—and when—to use them. In the Math Test – Calculator portion of the test, you’ll focus on complex modeling and reasoning, using your calculator to save time.
However, like any tool, the calculator is only as smart as the person using it. The Math Test includes some questions where it’s better not to use a calculator, even though you’re allowed to. In these cases, students who make use of structure or their ability to reason will probably finish before students who use a calculator.
The Math Test – No Calculator portion of the test makes it easier to assess your fluency in math and your understanding of some math concepts. It also tests well-learned technique and number sense.
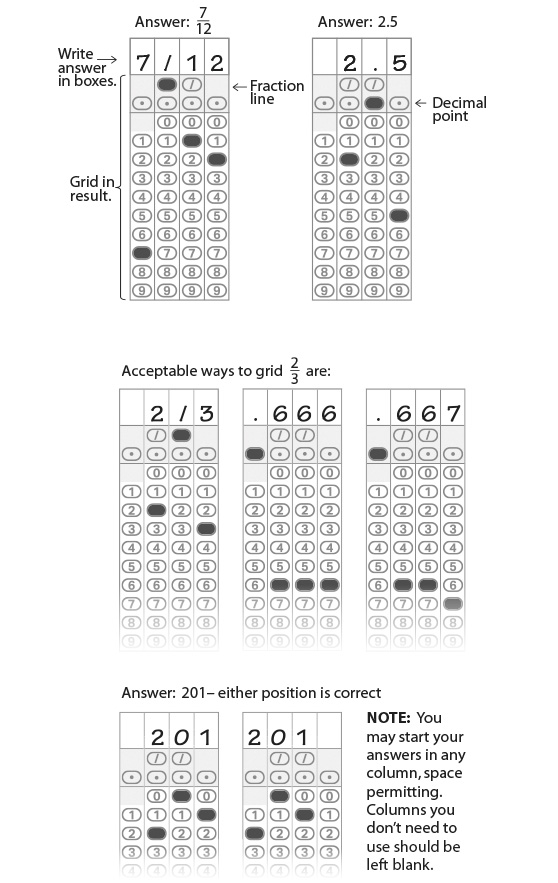
Grid-Ins
Although most of the questions on the Math Test are multiple choice, about 20% are student-produced response questions, also known as grid-ins. Instead of choosing a correct answer from a list of options, you solve problems and enter your answers in the grids provided on the answer sheet.
Gridding-In Answers
- Mark no more than 1 bubble in any column.
- Only answers indicated by filling in the bubble will be scored (you won’t receive credit for anything written in the boxes above the bubbles).
- It doesn't matter which column you begin entering your answers; as long as the responses are in the grid area, you’ll get credit.
- The grid can hold only 4 decimal places and can accommodate only positive numbers and zero.
- Unless a problem indicates otherwise, answers can be entered on the grid as a decimal or a fraction.
- Fractions like 3 over 24 do not need to be reduced to their lowest terms.
- All mixed numbers need to be converted to improper fractions before being recorded in the grid.
- If the answer is a repeating decimal, grid the most accurate value the grid will accommodate.
These instructions are an example of what you’ll see on the test: